O auditor de controle externo Luís, do Tribunal de Contas de um estado brasileiro, está conduzindo auditoria operacional em uma empresa pública estadual responsável pela gestão de um grande terminal portuário.
Durante a auditoria, verifica-se que a empresa, embora regida pelo direito privado, é majoritariamente controlada pelo Estado, que detém 85% de suas ações. Luís constata que a empresa não realizou licitação pública para a contratação de obras de ampliação do terminal e que o contrato foi firmado com uma empreiteira pertencente a ex-dirigentes da estatal, com indícios de superfaturamento.
A auditoria interna da empresa havia alertado para os riscos dessa contratação, mas seus relatórios foram ignorados pela alta direção. Diante disso, o auditor Luís pretende:
(I) aprofundar a auditoria sobre a legalidade e a eficiência da contratação;
(II) requisitar diretamente os documentos e justificativas à diretoria da empresa;
(III) propor medidas de ressarcimento e responsabilização;
(IV) publicar relatório parcial com os achados relevantes.
Com base na situação descrita e na Declaração de Lima, assinale a alternativa correta.
O Microsoft Teams, em sua configuração original, tem a funcionalidade de lobby, ou sala de espera, na realização de reuniões. Supondo que uma organização pretende realizar uma reunião por meio do aplicativo, assinale a alternativa correta acerca dessa funcionalidade, na configuração padrão.
A média aritmética de 4 números inteiros positivos é 9. A mediana da lista formada por eles vale 8.
Se a diferença entre o maior e o menor desses números é igual a 10, então o maior deles é
Analise as afirmativas a seguir, as quais versam sobre centralização e descentralização administrativa, marque V para as verdadeiras e F para as falsas:
( ) Na descentralização administrativa, há distribuição de competências para outra pessoa jurídica, enquanto na desconcentração ocorre apenas a distribuição interna de competências dentro de um mesmo ente.
( ) A descentralização por colaboração ou por delegação ocorre quando o Estado transfere para outra pessoa jurídica a titularidade e a execução de determinado serviço público.
( ) A centralização administrativa caracteriza-se pelo exercício direto das funções pelo próprio ente estatal, sem a delegação de competências a outras entidades.
( ) Na descentralização por serviço, técnica, funcional ou por outorga, conforme doutrina dominante, o Estado transfere para outra pessoa jurídica somente a execução de determinado serviço público, mantendo a titularidade para si.
Assinale a alternativa que apresenta a sequência correta de julgamento:
A Casa da Esperança é uma organização assistencial, sem fins lucrativos, mantida pela Igreja Deus de Todos, localizada no Município Alfa, e que se dedica a amparar pessoas em situação de vulnerabilidade social. Recentemente, os gestores da instituição receberam a cobrança do IPTU referente ao imóvel onde desenvolvem suas atividades. Diante dessa situação, considerando as disposições constitucionais, assinale a alternativa correta.
A Instrução Normativa FUNAI nº 02/2015 estabelece critérios e procedimentos para a proteção e monitoramento das terras indígenas no âmbito do licenciamento ambiental de empreendimentos. Assim, analise as afirmativas a seguir.
I. O licenciamento ambiental de empreendimentos que impactam terras indígenas deve considerar a Consulta Prévia, Livre e Informada às comunidades afetadas.
II. A compensação ambiental de impactos sobre terras indígenas é feita por meio de pagamento direto às comunidades, sem necessidade de mediação estatal.
III. Os estudos de impacto ambiental devem conter o Componente Indígena, que analisa os efeitos da obra sobre as populações e seus territórios.
Está correto o que se afirma em:
Uma sociedade de economia mista controlada pelo Estado de São Paulo contratou, sem licitação, serviços de sua subsidiária integral. Considerando essa situação, é correto afirmar que
Faz parte das responsabilidades da Comissão de Valores Mobiliários:
O processo de tomada de contas abrange os ordenadores de despesa, gestores e demais responsáveis por bens e valores públicos da administração direta e autarquias, empresas públicas, sociedades de economia mista e fundações instituídas ou mantidas pelo Poder Público estadual ou municipal, sendo instruído no setor competente daqueles órgãos, que o encaminhará ao Tribunal de Contas para julgamento.
A respeito desse processo, com base na Lei Complementar nº 709/1993, do Estado de São Paulo, é correto afirmar que:
Uma análise investiga o tempo de processamento de declarações de imposto de renda, em dias, para uma determinada população. Sabe-se que o tempo médio para processamento é de 11 dias e o desvio padrão é de 3 dias. Sejam os seguintes valores da distribuição normal padrão acumulada φ(0) = 0,5000, φ(1) = 0,8413, φ(2) = 0,9772 e φ(3) = 0,9987, em que φ(z) = P(–∞ < Z ≤ z). Considerando a distribuição normal para modelar o tempo de processamento, é correta a afirmativa que estima que
Durante auditoria realizada no contrato de fornecimento de merenda escolar firmado pela Prefeitura X, os auditores públicos realizaram diversos procedimentos, incluindo visitas a escolas para observar, em tempo real, a entrega dos alimentos por parte da empresa contratada, verificando horário, quantidade e forma de armazenamento.
Com base nessa informação, assinale a alternativa que apresenta corretamente o procedimento de auditoria descrito.
Um órgão público assinou um contrato, após longo processo licitatório, que previa a aquisição de até 1.200 licenças de sistema operacional. Sabe-se que o custo unitário dessas licenças era de R$ 450,00 cada, conforme instrumento jurídico. Em 01.12.2023, 630 licenças foram colocadas em uso e classificadas como de licenças operacionais de prazo definido, em virtude de o prazo de utilização ser de 24 meses após sua ativação. Em 01.02.2024, com a posse dos novos servidores nomeados no último concurso, foram ativadas mais 120 novas licenças, com o mesmo prazo de expiração. Em 31.12.2024, o contador da unidade verificou que o valor em uso dessas licenças era de R$ 500.000,00 e que o valor de mercado totalizava R$ 262.500,00.
Em 31.12.2024, quanto será o ajuste a valor recuperável das licenças a ser reconhecido nas demonstrações contábeis, em reais?
Na elaboração das etapas do Plano de Gerenciamento de Resíduos da Construção Civil, existe a determinação de que os geradores de resíduos (pessoas, físicas ou jurídicas, públicas ou privadas, responsáveis por atividades ou empreendimentos que gerem os resíduos) devem garantir o confinamento dos resíduos da geração até a etapa de transporte, assegurando, em todos os casos possíveis, as condições de reutilização e de reciclagem, essa etapa é denominada de
Conforme o normativo brasileiro, qualquer pessoa física ou jurídica, pública ou privada, que utilize, arrecade, guarde, gerencie ou administre dinheiros, bens e valores públicos deve prestar contas.
Entre essas pessoas passíveis de fiscalização pelos órgãos de controle, encontram-se as associações públicas que são uma espécie de
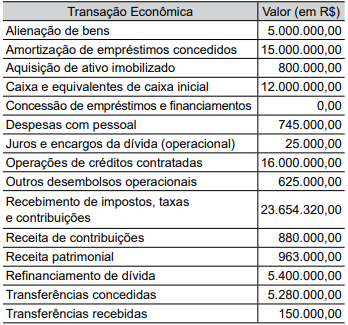
Quanto totalizou o saldo final de caixa e equivalentes de caixa, em reais?