No que diz respeito à relação professor-estudante no ambiente educativo, julgue o item subsecutivo.
A função docente requer um distanciamento emocional que garanta a autoridade do professor no contexto da sala de aula.
Com relação à didática na formação do professor, julgue o item a seguir.
A didática é uma disciplina prática, sem interseção com as disciplinas teóricas.
Com relação à didática na formação do professor, julgue o item a seguir.
A dinâmica da relação professor-estudante é fundamental para a ação didática.
The words “longing”, “change”, “myself” and “hardcore”, underlined in the text, are respectively:
The World’s strangest laws
1. You can’t call a pig Napoleon in France.
2. It is illegal to die in the Houses of Parliament.
3. In Miami, Florida, you mustn’t skateboard in a police station.
4. In London, you don’t have to pay to take a flock of sheep across London Bridge.
5. In Florida, unmarried women can’t parachute on Sundays.
6. It’s illegal to play golf on the streets of New York.
7. In Kentucky the law still says that everyone must have a bath at least once a year.
8. In seventeenth-century Russia, you couldn’t grow a beard unless you paid a special tax.
9. In fifteenth-century England, it was illegal for men to wear a moustache.
10. In the USA in the eighteenth century, bars couldn’t sell soda water on Sundays.
From the book Practical Grammar John Hughes and Ceri Jones
According to the text, choose the correct alternative:
Life on a desert island
Alexander,L.G.
Most of us have formed an unrealistic picture of life on a desert island. We sometimes imagine a desert island to be a sort of paradise where the sun always shines. Life there is simple and good. Ripe fruit falls from the trees and you never have to work. There is also the other side of the picture: Life on a desert island is wretched - you either starve to death or live like Robison Crusoe waiting for a boat which never comes. Perhaps there is an element of truth in both these pictures, but few of us have had the opportunity to find out.
Two men who recently spent five days on a coral island whished they had stayed there no longer. They were taking a badly damaged boat from the Virgin Islands to Miami to have it repaired. During the journey, their boat began to sink. They quickly loaded a small rubber dinghy with food, matches, and cans of beer and rowed for a few miles across the Caribbean until they arrived at a tiny coral island. There were hardly any trees on the island and there was no water to drink, but this didn’t prove to be a problem since the men collected rain-water in the rubber dinghy. As they
had brought a spear gun with them, they had plenty to eat. They caught lobster and fish every day, and, as one of them put it, “ate like kings”. When a passing tanker rescued them five days later, both men were genuinely sorry that they had to leave.
New concept English. Developing skills: an integrated course for intermediate students.
“Life there is simple and good. Ripe fruit falls from the trees and you never have to work.” These sentences could be connected by the word:
The lion and the four bulls
Clarke, M.
A lion used to walk about a field in which four bulls lived. Many times he tried to attack them, but whenever he came near, they turned their tails toward one another so that whichever way the lion tried to attack, he would have to face the horns of one of them.
At last, however, the bulls started arguing with each other, and each went off to a different part of the field by himself. Then the lion attacked them one by one and soon had killed all four.
Ann Arbor: The University of Michigan Press, 1996.p.138
The messsage of the text can be summarized as:
Insomnia
Insomnia is the most common of all sleep complaints. Almost everyone has occasional sleepless nights, perhaps due to stress, heartburn or drinking too much caffeine or alcohol. Insomnia is a lack of sleep that occurs on a regular or frequent basis, often for no apparent reason.
How much sleep is enough varies. Although 7 1/2 hours of sleep is about average, some people do fine on 4 or 5 hours of sleep. Other people need 9 or 10 hours a night.
Inability to get a good night’s sleep can affect not only your energy level and mood but your health as well because sleep helps bolster your immune system. Fatigue, at any age, leads to diminished mental alertness and concentration. Lack of sleep is linked to accidents both on the road and on the job.
About one out of three people have insomnia sometime in their life. Sleeplessness may be temporary or chronic. You don’t necessarily have to live with sleepless nights. Some simple changes in your daily routine and habits may result in better sleep.
htttp://www.mayoclinic.com.
The text contains information on:
‘Emily in Paris’ star says he partly understands why critics panned the ‘cliché’ Netflix show
Despite being a huge hit for Netflix, critics across the board (particularly French critics) have slammed the show for indulging in outdated and offensive stereotypes that present Parisians as rude, sexist, and elitist.
The main love interest in Netflix’s controversial comedy “Emily in Paris” said he partly understands why critics have panned the show. “I think they’re right in a way,” Lucas Bravo, who plays chef Gabriel in the show, said during an interview with Cosmopolitan.
The 32-year-old French actor continued: “At some point, if you want to tell a story about Paris, you have to choose an angle. You have to choose a vision. French critics, they didn’t understand the fact that it’s just one vision. They’re like, ‘Oh, this is not what Paris is.’ Of course. Paris is many things.”
Adapted from https://www.insider.com/emily-in-paris-star-lucas-bravounderstands-netflix-show-criticism-2020-10.
In the sentence “At some point, if you want to tell a story about Paris, you have to choose an angle”, the words “have to” could be substituted by:

About ideas stated in the text above and the words used in it, judge the following items.
There are places in the world where wind power works well in freezing temperatures.
In the fragment from the first paragraph “A number of authors have challenged longstanding cognitivist orientations of SLA”, the underlined term refers to cognitivist orientations which
How facial recognition technology aids police

Police officers’ ability to recognize and locate individuals with a history of committing crime is vital to their work. In fact, it is so important that officers believe possessing it is fundamental to the craft of effective street policing, crime prevention and investigation. However, with the total police workforce falling by almost 20 percent since 2010 and recorded crime rising, police forces are turning to new technological solutions to help enhance their capability and capacity to monitor and track individuals about whom they have concerns.
One such technology is Automated Facial Recognition (known as AFR). This works by analyzing key facial features, generating a mathematical representation of them, and then comparing them against known faces in a database, to determine possible matches. While a number of UK and international police forces have been enthusiastically exploring the potential of AFR, some groups have spoken about its legal and ethical status. They are concerned that the technology significantly extends the reach and depth of surveillance by the state.
Until now, however, there has been no robust evidence about what AFR systems can and cannot deliver for policing. Although AFR has become increasingly familiar to the public through its use at airports to help manage passport checks, the environment in such settings is quite controlled. Applying similar procedures to street policing is far more complex. Individuals on the street will be moving and may not look directly towards the camera. Levels of lighting change, too, and the system will have to cope with the vagaries of the British weather.
[…]
As with all innovative policing technologies there are important legal and ethical concerns and issues that still need to be considered. But in order for these to be meaningfully debated and assessed by citizens, regulators and law-makers, we need a detailed understanding of precisely what the technology can realistically accomplish. Sound evidence, rather than references to science fiction technology --- as seen in films such as Minority Report --- is essential.
With this in mind, one of our conclusions is that in terms of describing how AFR is being applied in policing currently, it is more accurate to think of it as “assisted facial recognition,” as opposed to a fully automated system. Unlike border control functions -- where the facial recognition is more of an automated system -- when supporting street policing, the algorithm is not deciding whether there is a match between a person and what is stored in the database. Rather, the system makes suggestions to a police operator about possible similarities. It is then down to the operator to confirm or refute them.
By Bethan Davies, Andrew Dawson, Martin Innes (Source: https://gcn.com/articles/2018/11/30/facial-recognitionpolicing.aspx, accessed May 30th, 2020)
The authors conclude the text by stating that
How facial recognition technology aids police

Police officers’ ability to recognize and locate individuals with a history of committing crime is vital to their work. In fact, it is so important that officers believe possessing it is fundamental to the craft of effective street policing, crime prevention and investigation. However, with the total police workforce falling by almost 20 percent since 2010 and recorded crime rising, police forces are turning to new technological solutions to help enhance their capability and capacity to monitor and track individuals about whom they have concerns.
One such technology is Automated Facial Recognition (known as AFR). This works by analyzing key facial features, generating a mathematical representation of them, and then comparing them against known faces in a database, to determine possible matches. While a number of UK and international police forces have been enthusiastically exploring the potential of AFR, some groups have spoken about its legal and ethical status. They are concerned that the technology significantly extends the reach and depth of surveillance by the state.
Until now, however, there has been no robust evidence about what AFR systems can and cannot deliver for policing. Although AFR has become increasingly familiar to the public through its use at airports to help manage passport checks, the environment in such settings is quite controlled. Applying similar procedures to street policing is far more complex. Individuals on the street will be moving and may not look directly towards the camera. Levels of lighting change, too, and the system will have to cope with the vagaries of the British weather.
[…]
As with all innovative policing technologies there are important legal and ethical concerns and issues that still need to be considered. But in order for these to be meaningfully debated and assessed by citizens, regulators and law-makers, we need a detailed understanding of precisely what the technology can realistically accomplish. Sound evidence, rather than references to science fiction technology --- as seen in films such as Minority Report --- is essential.
With this in mind, one of our conclusions is that in terms of describing how AFR is being applied in policing currently, it is more accurate to think of it as “assisted facial recognition,” as opposed to a fully automated system. Unlike border control functions -- where the facial recognition is more of an automated system -- when supporting street policing, the algorithm is not deciding whether there is a match between a person and what is stored in the database. Rather, the system makes suggestions to a police operator about possible similarities. It is then down to the operator to confirm or refute them.
By Bethan Davies, Andrew Dawson, Martin Innes (Source: https://gcn.com/articles/2018/11/30/facial-recognitionpolicing.aspx, accessed May 30th, 2020)
The word that may replace “In fact” in “In fact, it is so important”, without change in meaning, is
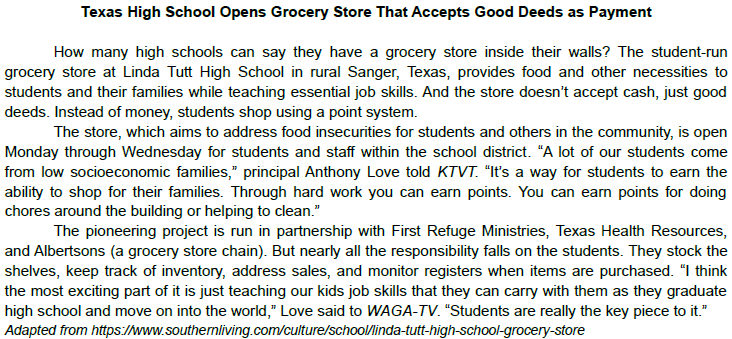
According to the text, “...stock the shelves...” (paragraph 3) is an example of