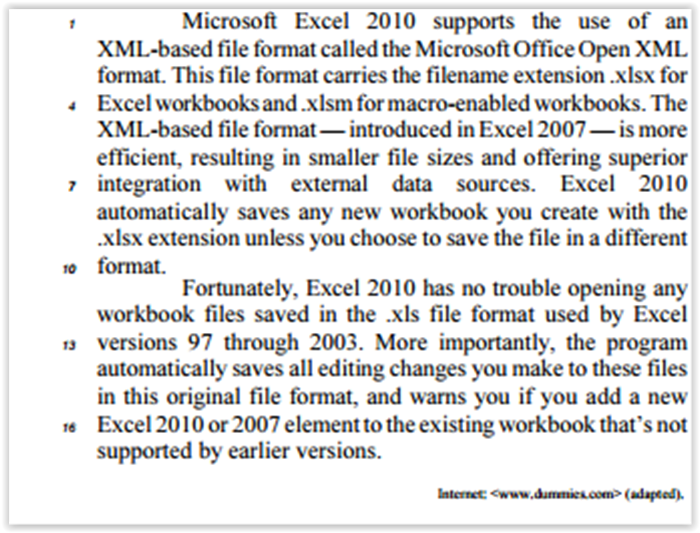
In the fragment of the text “Thankfully, this time around, the
outlook for renewable energy isn't so bleak" (lines 11-12), the
word bleak can be replaced, with no change in meaning, by
On the ideas of the text and the vocabulary used in it, judge the next items.
Replacing “earlier” (l.17) by older changes the meaning of the last sentence of the text.

In the text CB3A1AAA,
the verb “realize” (l7) can be replaced by accomplish without any change in the meaning of the sentence.
The phrase “stunted professional growth” implies that professional growth may be
The phrase “lots of data to chew on” in Text II makes use of figurative language and shares some common characteristics with:
The phrase “lots of data to chew on” in Text II makes use of figurative language and shares some common characteristics with:
When Text II mentions “grumblers” in “to face the grumblers”, it refers to:
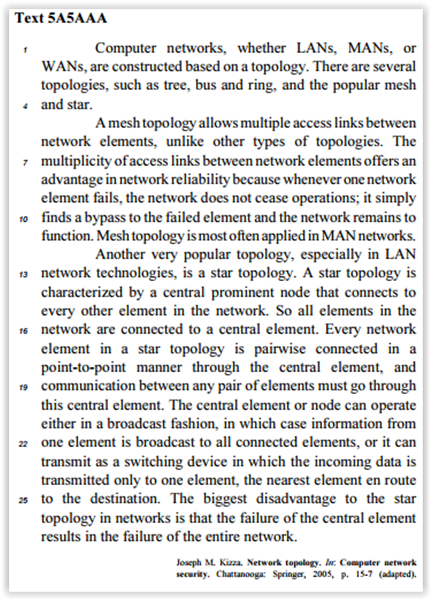
In the text 5A5AAA,
“en route" (R.24) can be replaced by on the way without any
change in the meaning of the sentence.
On the ideas of the text and the vocabulary used in it, judge the next items.
In line 9, “unless” can be correctly replaced by except if.
The phrase “lots of data to chew on” in Text II makes use of figurative language and shares some common characteristics with:
The phrase “lots of data to chew on” in Text II makes use of figurative language and shares some common characteristics with:
READ TEXT II AND ANSWER QUESTIONS 21 TO 25:
TEXT II
The backlash against big data
[…]
Big data refers to the idea that society can do things with a large
body of data that weren't possible when working with smaller
amounts. The term was originally applied a decade ago to
massive datasets from astrophysics, genomics and internet
search engines, and to machine-learning systems (for voicerecognition
and translation, for example) that work
well only when given lots of data to chew on. Now it refers to the
application of data-analysis and statistics in new areas, from
retailing to human resources. The backlash began in mid-March,
prompted by an article in Science by David Lazer and others at
Harvard and Northeastern University. It showed that a big-data
poster-child—Google Flu Trends, a 2009 project which identified
flu outbreaks from search queries alone—had overestimated the
number of cases for four years running, compared with reported
data from the Centres for Disease Control (CDC). This led to a
wider attack on the idea of big data.
The criticisms fall into three areas that are not intrinsic to big
data per se, but endemic to data analysis, and have some merit.
First, there are biases inherent to data that must not be ignored.
That is undeniably the case. Second, some proponents of big data
have claimed that theory (ie, generalisable models about how the
world works) is obsolete. In fact, subject-area knowledge remains
necessary even when dealing with large data sets. Third, the risk
of spurious correlations—associations that are statistically robust
but happen only by chance—increases with more data. Although
there are new statistical techniques to identify and banish
spurious correlations, such as running many tests against subsets
of the data, this will always be a problem.
There is some merit to the naysayers' case, in other words. But
these criticisms do not mean that big-data analysis has no merit
whatsoever. Even the Harvard researchers who decried big data
"hubris" admitted in Science that melding Google Flu Trends
analysis with CDC's data improved the overall forecast—showing
that big data can in fact be a useful tool. And research published
in PLOS Computational Biology on April 17th shows it is possible
to estimate the prevalence of the flu based on visits to Wikipedia
articles related to the illness. Behind the big data backlash is the
classic hype cycle, in which a technology's early proponents make
overly grandiose claims, people sling arrows when those
promises fall flat, but the technology eventually transforms the
world, though not necessarily in ways the pundits expected. It
happened with the web, and television, radio, motion pictures
and the telegraph before it. Now it is simply big data's turn to
face the grumblers.
(From http://www.economist.com/blogs/economist explains/201
4/04/economist-explains-10)
The use of the phrase “the backlash” in the title of Text II means the:
The word ‘robust’ (l.15) can be correctly replaced by effective without this bringing any change of meaning to the sentence.

Judge the next items according to the text presented on cyber-ethics.
The expression “In a nutshell” (R.14) introduces a summarized and simplified version of what cyber-ethics is all about.

Mining tourism in Ouro Preto
Ouro Preto is surrounded by a rich and varied natural
environment with waterfalls, hiking trails and native vegetation
partially protected as state parks. Parts of these resources are
used for tourism. Paradoxically, this ecosystem contrasts with the
human occupation of the region that produced, after centuries, a
rich history and a cultural connection to mining, its oldest
economic activity which triggered occupation. The region has an
unlimited potential for tourism, especially in specific segments
such as mining heritage tourism, in association or not with the
existing ecotourism market. In fact, in Ouro Preto, tourism,
history, geology and mining are often hard to distinguish; such is
the inter-relationship between these segments.
For centuries, a major problem of mining has been the reuse of
the affected areas. Modern mining projects proposed solutions to
this problem right from the initial stages of operation, which did
not happen until recently. As a result, most quarries and other
old mining areas that do not have an appropriate destination
represent serious environmental problems. Mining tourism
utilizing exhausted mines is a source of employment and income.
Tourism activities may even contribute to the recovery of
degraded areas in various ways, such as reforestation for leisure
purposes, or their transformation into history museums where
aspects of local mining are interpreted.
Minas Gerais, and particularly Ouro Preto, provides the strong
and rich cultural and historical content needed for the
transformation of mining remnants into attractive tourism
products, especially when combined with the existing cultural
tourism of the region. Although mining tourism is explored in
various parts of the world in extremely different social, economic,
cultural and natural contexts, in Brazil it is still not a strategy
readily adopted as an alternative for areas affected by mining
activities.
(Lohmann, G. M.; Flecha, A. C.; Knupp, M. E. C. G.; Liccardo, A.
(2011). Mining tourism in Ouro Preto, Brazil: opportunities and
challenges. In: M. V. Conlin; L. Jolliffe (eds). Mining heritage and
tourism: a global synthesis. New York: Routledge, pp. 194-202.)
The opposite of the underlined word in “are often hard to distinguish” (l. 11) is: